THIS IS HOW YOU TAKE PROPER CARE OF YOUR KNIFE
TIPS FROM THE PRO
Knives are used in all kitchens on a daily basis. They are indispensable for processing food.
We will give you some tips on how to take care of your knives so that you have many years of enjoyment with your sharp knives.
WASHING BY HAND / DISHWASHER

Rinse directly after use
The first rule of knife care: Do not leave any food residues on your knife, but clean it directly after use. Rinse off any food residues containing salt or acid. This is especially important when the knife comes into contact with fruit acids, such as fruit or vegetable juices and food containing salt, such as mustard or ketchup. Use a mild dish-washing detergent and then dry it with a soft cloth.
Running water, soft Cloth
If possible, wash your knives by hand. We recommend using a mild detergent under running water with a soft cloth. This way, you avoid submitting the blade to aggressive detergents or chlorinated water for longer periods of time. After cleaning, carefully dry the knife, which prevents stains on the blade that accumulate as a result of the natural deposits of limy water.
Dishwasher suitable
Our knives with plastic handles are generally suitable for the dishwasher; however we do recommend washing them by hand. This helps prevent stains and the accumulation of extraneous rust and avoids damage to the blades.
Highly concentrated detergent
Please note that cleaning in the dishwasher is much more aggressive than cleaning by hand. This is because of the highly concentrated dish-washing detergents. Leaving knives in the hot and steamy dishwasher can also lead to staining on the blade. Plus the fine cutting edge in the outer area is slightly bent in the dishwasher, which reduces the knife's cutting properties.
Cutlery in the dishwasher / tips for the dishwasher
Start the cleaning program as soon as you have filled the dishwasher with knives. Choose an appropriate program and do not sort the knives directly above the heating spiral. Once the washing cycle is complete, quickly remove the knives and dry them, if necessary, by hand.
CUTTING BOARD
We recommend using a wooden or plastic board for cutting. Please never cut on a plate, on metal or on stone! If hard substances are used to cut on, such as marble, granite or glass, the cutting edges will become quickly blunt.
These materials are frequently used for cutting for the sake of hygiene, the knives however wear off, which is highly undesired.
STORAGE
Always keep your knives in a safe and dry place. The blades are well protected in a knife block. Knives that are stored in the drawer should be protected with protective sleeves for blades.
SHARPENING / WHETTING
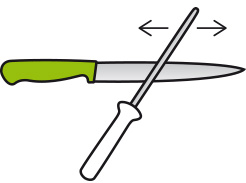
We recommend using a whetting iron / whetting rod as an aid. It is made of extremely hard steel. To improve the cutting quality of knives, have your blades whetted, or straightened, as professionals would say. Because a whetting steel does not wear any material off of the blade, but rather it straightens out the cutting edge. This microscopic bending occurs when the knife is used.
To sharpen the knife, the whetting rod is held at an angle of approx. 20 degrees on the blade and moved with slight pressure from the knife handle to the tip of the knife on both sides. Please note: Always perform grinding movements directed away from the body.
Sharpening knives with a whetting rod is only suitable for knives with a straight edge (grind). Knives with a serrated edge, such as bread knives or vegetable cutters with a sawtooth edge cannot be sharpened with a whetting iron.
RUST STAINS
How do rust stains arise?
Dishes and cutlery are often cleaned in the dishwasher at night. The knives are therefore in the machine for a longer period of time. While cooling off, rust stains may also appear on non-corrosive knives and flatware.
Extraneous rust or rust film
Rust stains on knives usually appear as a result of extraneous rust or rust film that is transferred from other objects in the dishwasher. Tiny rust particles become detached from pots and pans equipped with handles or screws that are not made of non-corrosive steel. Other sources of rust can made by damaged enamelled kitchen appliances or kitchen utensils made of low-alloy steels, such as tea strainers. Dish racks can give off rust particles if the plastic coating of the metal rods is damaged.
The rust that is produced is distributed throughout the dishwasher and it becomes attached to non-corrosive steels. In rare cases however, rust can also be formed via tap water.
Removing rust stains
Rust stains can be removed by cleaning the blade with a sponge or dishcloth and some scouring cream or metal cleaner. In the case of stubborn stains, we recommend using a metal polish. A small spot that is still visible will not have further consequences if the blade is kept dry.
Why can rust accumulate on non-corrosive steels?
Blade steel must comply with certain quality requirements so that the knives have optimum cutting properties and good rust resistance. In order to bear the name "Solingen", the quality of the blade must comply with the requirements stipulated in the standard of DIN ISO 8442-1. Martensitic carbon steel is required for the production of blades of the type 1.4034 (X46CR13) as minimum quality. The carbon content is approx. 0.46 % and the chrome content is approx. 13%.
Chrome and carbon content can have a positive as well as a negative influence on the quality of the blade: Carbon guarantees the cutting performance or cutting properties and hardness of a blade. However, these properties also have the following consequences: the more carbon a steel contains, the more susceptible it is to rust. Chrome on the other hand, reduces a blade's susceptibility to rust. But: the more chrome is contained in steel, the weaker the cutting performance and hardness is.
A good knife is therefore always a compromise, depending on whether better cutting properties or higher rust resistance is desired. Therefore, so-called "non-corrosive" knives can accumulate rust stains, point corrosion or also rust film (extraneous rust). If proper care is given, so-called non-corrosive knives are hardly susceptible to rust. The above care recommendations should be observed to ensure long and good cutting properties of knives.

